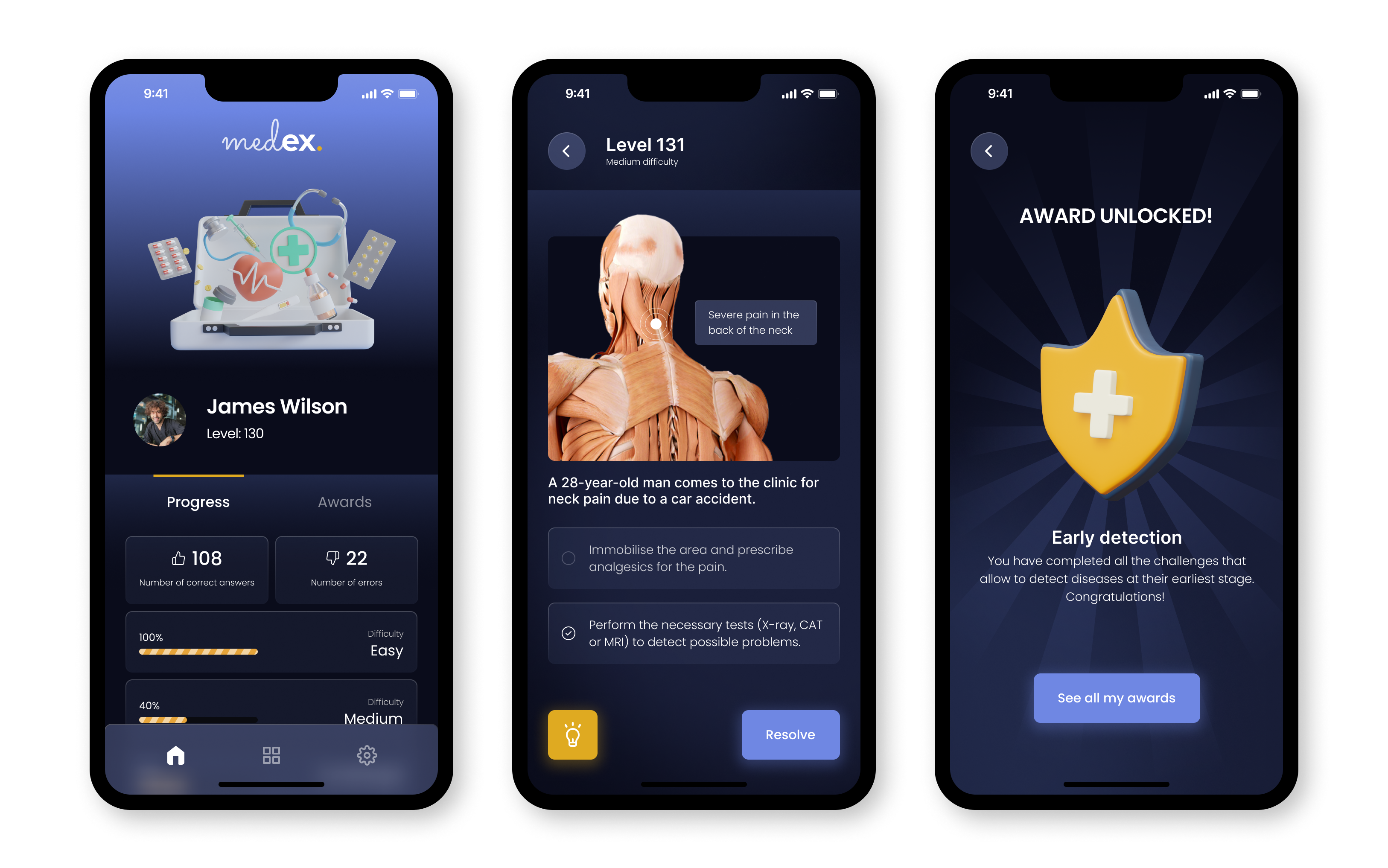
Gamified solutions have become a popular tool for training and education in a variety of industries, including healthcare. By even just incorporating simple mechanics such as levels that break down learning materials, interactive quizzes to test knowledge, and engaging, energising game-like experiences, gamification can facilitate a more effective way to teach complex concepts and procedures. They can also provide a safe, low-risk environment for learners to practice and make mistakes without real consequences. Online games have been used to train healthcare professionals in areas such as infection control, patient communications and emergency response. In appropriate settings, the use of gamification as a training tool for healthcare professionals can contribute towards improving the quality of support and patient care, as more engaging and effective study methods help improve the retention of knowledge and skills needed for safe and effective treatment.
The importance of training in the healthcare sector
Continuous training and educational support systems are crucial for healthcare professionals to provide the best possible care for patients. While healthcare is constantly evolving through valuable research and breakthroughs, it is also a sector under tremendous pressure in terms of time, resourcing, and investment. It is understandable that medical and care professionals need to stay up to date with new information or emerging technologies that can help improve patient outcomes or even make their own day-to-day work easier, but for the majority and especially those on the front line, it is hard to find time to squeeze extra work in. Even just with the rise of electronic records and online medical services, ongoing training is essential, but also amounting, for staff to keep up with these changes all while provide optimal treatment.
Faced with little time, high stress, and working days that require great focus and attention, traditional methods of healthcare training, such as lectures, textbooks and seminars, may be less effective and less engaging. These methods often do not offer opportunities for hands-on practice and tend to be less interactive, making it harder to retain information or consider how it works in practice. Digital or gamified approaches to learning can present simulated but realistic scenarios where the learner can test their understanding of core concepts, put theory into practice, or run through example situations to improve knowledge retention – particularly valuable for nuanced or less theory-based areas of learning, such as communication, collaboration or leadership skills for example.
“Understanding the different ways of learning, motivations and preferences of different users increases engagement and improves the learning process. At Motivait we try to use eye-catching designs, compelling narratives and gamification elements help the user to delve deeper into more complex topics.”
Whether mobile or desktop based, digital solutions can leverage the agility and accessibility of technology to instantly make learning paths available to learners whether they’re on the go and wanting to squeeze in 5 minutes on a quick course module, or in a more relaxed environment and keen to look at information in a different, more dynamic way. While the market may be saturated with options, there is no denying that one of the benefits to digital or online based learning approaches is that they can take into account different learning styles, which may make it easier for some people to learn more effectively. Certain learners may prefer hands-on learning, while others lean toward visual or auditory learning.
Then, by taking digital learning and training methods one step further to include gamification, the experiences can cater to diverse learning needs while also providing a much-needed support to driving sustainable engagement throughout the learning process. Game elements such as tracking progress to encourage participation, providing feedback, nudges or prompts to avoid people feeling lost or unsupported, or even just offering warm up rounds or quick game-like experiences to boost motivation can go a long way to enriching the learning journey for participants faced with complex or time-consuming themes as seen in healthcare.
Gamification in action
So, what can gamified solutions look like in practise?
A clear example of this can be seen in an innovative app that uses gamification to reduce unnecessary procedures in the Spanish National Health System. Created by a team of experts from the Ramón y Cajal University Hospital, FISABIO and the Miguel Hernández University, the app seeks to reduce procedures linked to ‘Do Not Do’ practices, in reference to all those unnecessary procedures that have been shown not to be useful, have questionable effectiveness, are not cost-effective or are not a priority. According to José Joaquín Mira, Professor of Health Psychology at the Miguel Hernández University:
“We have chosen to use gamification to draw attention to the problem of overuse of certain practices in a fun and practical way… It actively engages the practitioner, sparks curiosity and invites them to compete with themselves while internalising what not to do to achieve safer practice and higher quality care”.
The app works through a reward system, with scores being stored and added to the user’s profile. In addition, in the game settings you can choose the level of difficulty of the questions, the field of speciality and whether they will be repeated in the future. There are more than 100 questions (on a wide range of practices, linked to different specialities). The user will have a justification for the answer, a link to the official recommendations document, and information on which scientific society endorses it.
Using a gamified solution in the learning process can be an effective tool for improving knowledge retention and performance on certain medical tasks. For example, a study published in BMC Medical Education found that medical students who played a game designed to teach cardiology concepts performed better on a post-exam than those who received traditional classroom instruction. Another study published in PMC PubMed Central found that nurses who participated in a game designed to simulate medication administration had a higher rate of correct medication administration than those who did not participate in the game.
Bringing theory to life, putting skills into practise
There are few sectors where training is so important as within healthcare. Whether in hospitals, care homes, local medical centres, or wherever their work takes them, health professionals are under pressure to stay informed and well versed in evolving approaches, processes and practices or even new legislation they are expected to follow. Recognising the fact that many organisations and institutions within the sector won’t be able to invest endlessly, what solutions that are provided need to be creative in ensuring they impact the learning experience.
The ripple effect of participating in a positive, enjoyable session or experience, as opposed to leaving feeling drained and disillusioned, means learners feel valued (“how great that my organisation chose to positively invest in me and understand my needs”) and well equipped to tackle future challenges and situation. Gamification may just be one tool of many able to invigorate digital or hybrid approaches to learning, but it is certainly one methodology with proven impact on user engagement and optimised knowledge retention. At the end of the day, given the hurdles and stresses healthcare professionals and students handle, delivering solutions that put them at the heart of the process for once could just make the difference to them.
If you are interested in learning more about how gamification and technology can improve the learning experience and engagement, check out our work in this area: