In an increasingly digital world, the education sector is in a period of transformation driven by technology and new working models and methods. This digital strategy requires flexible education that encourages students and academic institutions to be active, innovative and entrepreneurial.
Electronic devices and the broader digital environment have become much more accessible to students. In terms of tools, technology has given rise to a wide range of platforms, equipment, systems, networks and applications that are already in use in many educational institutions and are expected to become even more common in the future. From the traditional textbook to a variety of digital materials, courses and support systems, content is expanding and diversifying.
As part of the Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027) the European Commission conducted a public consultation at the end of 2020 to obtain the views and experiences of citizens, institutions and organisations on the impact of COVID-19 on education and training, the consequent evolution towards remote and online learning, and the future of digital education in Europe.
Respondents expressed that online learning resources and content should be more relevant, interactive and user-friendly, and not dependent on the financial resources of a city or local council. More than 60% felt that their digital skills had improved during the pandemic, and more than 50% confirmed that they wanted to improve them further.
The study conducted in the Action Plan helps to reiterate the current trend towards online and hybrid learning that has been accelerated by events in recent years. These changes have led to the discovery of new and innovative ways in which learners and educators organise their online learning and teaching activities, engaging in more personal and flexible interactions
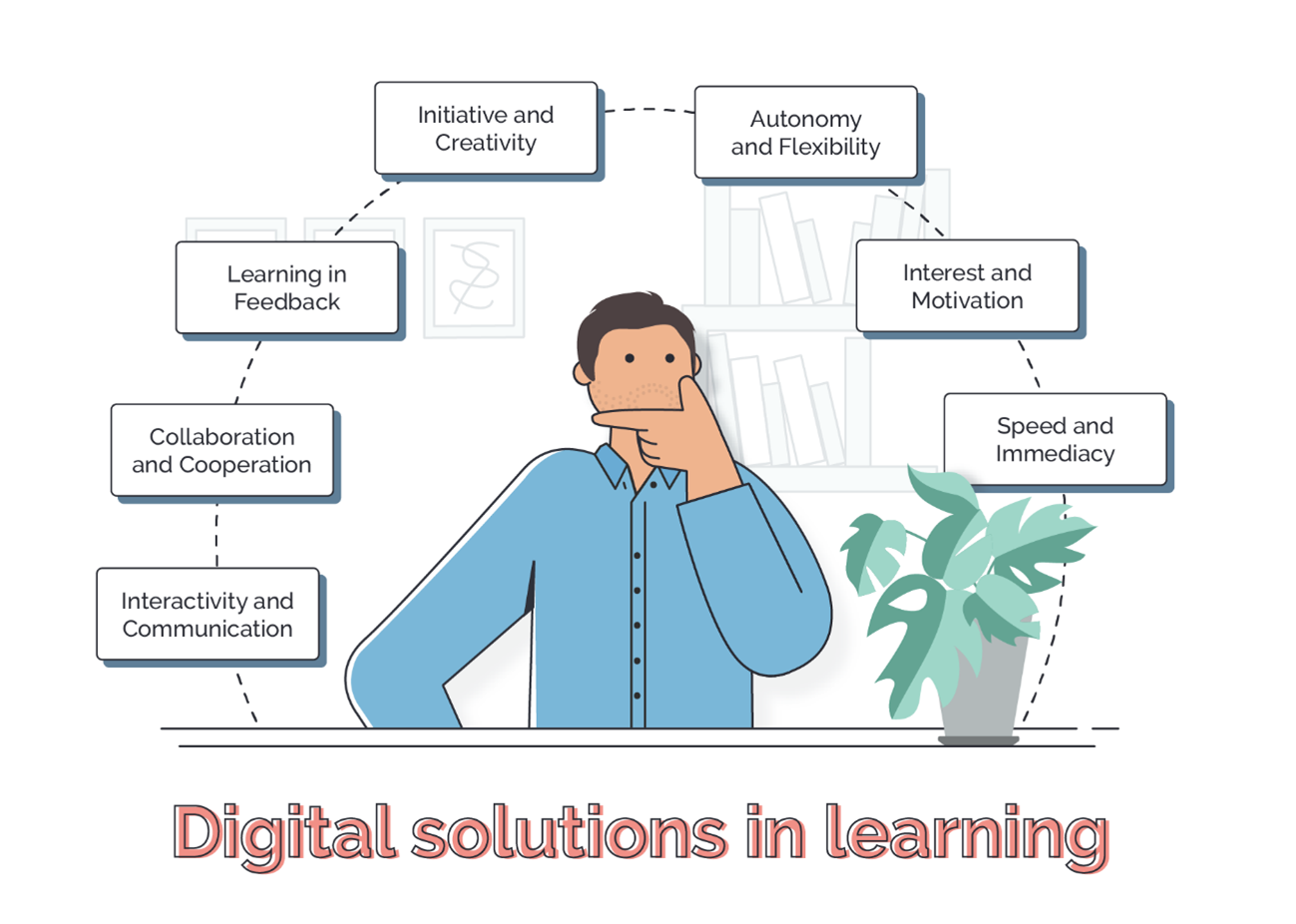
Support and motivate students with digital technology
Digital motivation is about applying the capabilities offered by new technologies to increase students’ confidence. Thus, making them feel more comfortable in their educational environment and ultimately improving their performance. Active engagement, cooperation among students, quick feedback on work or assessments, and the ability to put what they learn into practice are some of the conditions for students to learn effectively using technology. Students’ lack of motivation is not only a barrier to understanding topics, but also a challenge for teachers in their everyday work.
Academic institutions can support students on a personal level while providing a comprehensive and integrated understanding of university systems. Digital and interactive portals provide connections to all relevant systems, as well as ‘live sections’ that display grades, upcoming assignments, timetables and other information and encourage participation before, during and after different activities. Access to information and course materials anytime, anywhere. A way of communicating with students and guiding them through their work giving them assistance, focus and reinforcement.
As shown in a study published by McGraw-Hill Education, students prefer digital learning to traditional learning. According to the study, 81% think digital learning technology is helping them improve their grades, and 71% say digital course materials have increased their engagement. The clear majority of students believe that digital learning technology has benefited their schoolwork by encouraging concept retention and improving grades, and that more than half (53%) of students feel much more motivated in classrooms that incorporate such tools.
Towards a new university student experience
Increasingly, students want higher education institutions to provide them with a personalised and individualised experience. They expect the same level of interaction and experience offered by consumer brands such as Amazon and Netflix. To respond to these needs, leaders at universities, business schools and other education institutions are beginning to see a connection between the student and the consumer, and how digital transformation is necessary to meet the demands and aspirations of today’s students.
Consequently, students no longer want to be treated uniformly and anonymously, but are looking for tailored notifications and suggestions, customized to their own interests, as well as a perfect experience. They want to be seen, heard and appreciated, as well as receive attention that is specific to them. According to the Connected Student Report, 90% of students want universities to interact with them as frequently as possible, using email, tailored communications and notifications, as well as other means. Around 40% say they would prefer more individualised communications, and 25% say they would like a more personalised university experience in general.
For a higher level of success, digital solutions must include procedures that encourage reciprocity and interaction, thereby increasing knowledge retention and avoiding monotony. It is essential to ensure that students apply what they have learned to solve problems, practice decision-making and skills development in a safe environment where their understanding can be tested.
At the same time, digital solutions can lead to improvements in educational institutions to operate more efficiently in capturing new students, in ensuring the performance of students along their journey and also in maintaining contact with alumni. In addition, they serve as a digital basis for 360-degree monitoring of the educational process. An integrated platform that allows students to customise their university experience from start to finish.
Some examples of the benefits are:
- Collaboration and cooperation: experiences, work and projects can be shared, facilitating engagement and joint learning.
- Autonomy and flexibility: there are a variety of methods through which information can be obtained, as well as sufficient freedom for their own organisation and planning. (Asynchronous education)
- Interactivity and communication: Students can connect and talk to their peers, greatly enhancing their ability to communicate and learn. Even student-teacher conversation can take place outside the classroom.
Gamification in education
Gamification is one of the educational innovation techniques that has provoked most interest and success in recent years. It is a method that consists of introducing game aspects and dynamics into the teaching and learning process. Examples include ‘scoreboards’ that record students’ scores in various activities, ‘badges’ that are awarded to students when they reach certain learning milestones, and the use of applications that allow multiple-choice tests to be transformed into interactive competitions.
Let’s imagine an immersive narrative (initial motivation) in which we find ourselves on a deserted island and, in order to survive, we have to go through different levels, challenges and obstacles. There are many elements and strategies that we can incorporate into the island to encourage motivation, reinforcement, various stimuli and a greater sense of involvement. For example, through interesting and fun activities for students to work on concepts and exercise the basic skills that the subject is intended to promote. As you explore the island you earn small rewards that give access to badges and levels; all achievements will be added to a scoreboard (increased participation, continuous reinforcement and short-term motivation). In addition, a help or hints option can be included in which students can ask for assistance from both the teacher and other students (social immediacy). Within each challenge or activity there may be the possibility for students to choose different options or routes, i.e. depending on their choice, they may reach one outcome or another. For each completed task, quality and immediate feedback can be received in order to learn beyond mistakes. The experience can also encourage group work and systems of competition between teams (team-based learning).
This immersive experience can be part of any academic subject and for students of different ages, from different levels of school to university, postgraduate courses, etc. It all depends on the narrative, the approach, the design concept, the catalysts, etc. that are applied in each case. A way to exceed the mastery of the concepts of a subject and to discover and intensify fundamental values of personality and teamwork.
Therefore, we can conclude that the education sector has undergone a significant digital transformation, encouraging both students and academic institutions to become more engaged, creative, and entrepreneurial. Learners and educators have discovered new and imaginative methods to organize their educational activities as a result of recent changes and adjustments during the pandemic. There is now a much easier access to electronic tools, and technology has resulted in a variety of platforms, equipment, systems, networks, and applications. Digital transformation is necessary to meet the demands and aspirations of today’s students, who are increasingly seeking a personalized and individualized experience and concepts such as gamification can further improve student performance and motivation while also making a topic more enjoyable.